As promised in “What’s the Biggest Cause of Fatty Liver Disease?” article, here is the article on how NAFLD/NASH is diagnosed.
When you go for a medical appointment to check for fatty liver disease, the doctor will go through procedures, e.g. taking of medical history, physical observation and diagnostic tests.
Read on!
Medical history
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease. The doctor will be asking about your history (and probably your family history) of any health-related conditions that increase your risk of developing NAFLD and NASH, like the following [1]:
- Overweight or obesity
- Insulin resistance
- High levels of triglycerides or abnormal levels of cholesterol in your blood
- Metabolic syndrome
- Type 2 diabetes
He/she will also ask about dietary and lifestyle factors that may make you more likely to develop NAFLD and NASH, e.g. a diet rich in added sugars, high in fat, or a lack of physical activity/exercise; cigarette smoking; any medications taken.
The doctor will ask about your alcohol consumption to check whether the fat in your liver is a sign of alcoholic liver disease or NAFLD as medical tests can’t show whether alcohol is the cause of the fat build up in your liver.
Physical exam / Observation
During a physical exam, the doctor typically checks your weight and height to calculate your body mass index (BMI). He/she observes your body and looks for signs of NAFLD or NASH, including [1]:
-
- An enlarged liver
Doctors use their fingertips to press on the right side of your abdomen just below your rib cage and palpate (feel/touch) the lower edge of your liver, perceiving its size, tenderness and texture. Depending on the primary cause, an inflamed liver may feel irregular, soft or firm. There might also be a presence of well-defined lumps. However, this procedure only provides a very rough estimate of liver size [2].
- Physical signs of insulin resistance e.g. darkened skin patches over the knees, elbows and knuckles.
- Physical signs of cirrhosis, such as jaundice, a condition where skin and white part of the eye turn yellow.
- An enlarged liver
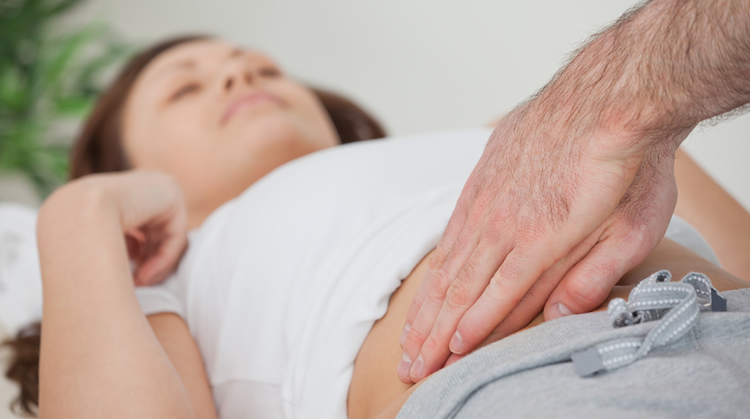

Tests to diagnose NAFLD and NASH
Doctors use blood tests, imaging tests, and sometimes liver biopsy to detect NAFLD and NASH in patients.
Blood Tests
A health care professional will take a blood sample from you and send it to a laboratory. Your doctor may suspect that you have NAFLD or NASH if your blood test result shows increased levels of the liver enzymes “alanine aminotransferase” (ALT) and “aspartate aminotransferase” (AST). The doctor may order further blood tests to check if you have other health conditions that may increase your liver enzyme levels.
Imaging tests
Your doctor may use the following imaging tests to help diagnose NAFLD:
-
- Ultrasound
This procedure uses a device called a transducer, which bounce painless and safe sound waves off your organs to create an image of their structure.
Here’s a quick overview video on abdominal ultrasound: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eM1qLM7VJw8
- Ultrasound
-
- Computerized tomography (CT) scans
CT scans are painless and non-invasive. Nowadays, with newer machines, the procedure takes only a few minutes. CT scans use a combination of x-rays and computer technology to generate images of the liver. They may be done with or without “contrast”. A health care professional may give you an injection of a special dye, called contrast medium, which helps to make the structures inside the body easier to see (or in some cases the contrast will be ingested by mouth).
You’ll be asked to remove any metal object from your body, e.g. jewelleries, then lie on a table that slides into a tunnel-shaped device that takes the scan.Here are two quick overview videos on CT Scan procedure:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zzKAyMuaP7M
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uHu9aa0QDiE
- Computerized tomography (CT) scans
-
-
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
This is also a non-invasive procedure. MRI machines use radio waves and magnets to produce detailed images of your organs and soft tissues without using x-rays. A health care professional may give you an injection of contrast medium. With most MRI machines, you’ll lie on a table that slides into a tunnel-shaped device. Some machines allow you to lie in a more open space. You may receive light sedation during an MRI if you have a fear of confined spaces (claustrophobia).
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
- A technician performs the MRI test in a hospital or radiology center. You may be given contrast as well. The machine will make loud buzzing and thumping noises as it takes images. Several hospitals offer headphones or earplugs to help minimize them.
-
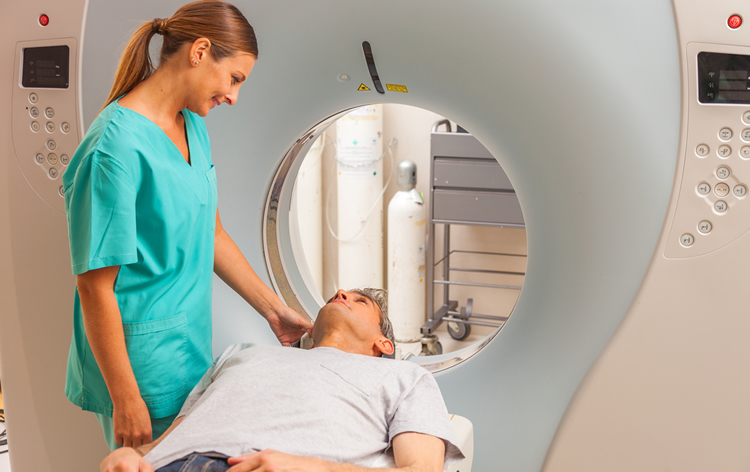
- MRI machines are very sensitive to movement, it’s important that the patient lie very still. The technician may also ask the patient to hold his/he rbreath for a few seconds as images are being taken [3].
Here’s a quick video overview of abdominal MRI: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T8JHrTOa1Q4
Imaging tests can show fat in your liver. But these tests cannot show inflammation or fibrosis in the liver. Therefore, your doctor cannot use these tests to conclude whether you have simple fatty liver or NASH.
Imaging test result showing nodules or lumps on your liver may indicate cirrhosis.
Liver biopsy
Your doctor may recommend a liver biopsy if you are more expected to have NASH or if your other tests show signs of cirrhosis or other advanced liver disease. A liver biopsy is the only way to detect liver inflammation and damage to diagnose NASH. Doctors don’t order this test for everyone with NAFLD.
A doctor performs a liver biopsy at an outpatient center or a hospital. A health care professional will tell you how to prepare for a liver biopsy. You may need to stop taking certain medicines to prepare. You may be asked to fast for 8 hours before the procedure. During the procedure, you may be given a local anesthesia, sedatives, and pain medicine.
During the biopsy, the patient will be asked to lie on a table with the right hand resting above the head. The doctor will numb the area where he or she will insert the biopsy needle with a local anesthetic and then use the needle to take a small piece of liver tissue. A pathologist will analyse it to look for signs of damage or disease.
Here’s a quick video summary of a liver biopsy procedure: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mnHPx5XEvfQ
Conclusion
Prevention is always better than cure, such a cliché, but worth the effort. We have explored Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and its diagnosis. Why go through all the trouble of getting sick when you can simply avoid it through healthy dietary and lifestyle practices? Or in case you already have it, you can prevent it to worsen and lose one of the most important things in life that cannot be bought: health.
Improve Your Liver Health NOW!

Do you have stubborn fat? Are you stuck on a plateau where no matter what you do, you just can’t lose weight?
LivLean, our best-selling blend of 15 all-natural ingredients, is clinically proven to promote liver health. LivLean Supports:
-
- Liver Health & Detoxification
-
- A Healthy Metabolism
-
- Immune Function
- Healthy, Normal Blood Sugar Levels
CLICK HERE TO LEARN MORE ABOUT LIVLEAN.
References
- The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health. (2016). Diagnosis of NAFLD and NASH. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/nafld-nash/diagnosis
- Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2017). Tests and Diagnosis. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/enlarged-liver/basics/tests-diagnosis/con-20024769
- Healthline Media. (2017). Abdominal MRI Scans. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/abdominal-mri-scan#procedure5
Videos
- [Mohammad Sadique]. (2014, July 31).General Ultrasound #1 Abdominal (Limited, Complete) [Video File]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eM1qLM7VJw8
- [Scottsdale Medical Imaging]. (2016, December 6). What to Expect During a CT Scan [Video File]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zzKAyMuaP7M
- [UWMedicineHealth]. (2010, December 20). CT (Computed Tomography Scan) [Video File]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uHu9aa0QDiE
- [MRI Michigan]. (2012, June 13). Abdominal MRI [Video File]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T8JHrTOa1Q4
- [Nucleus Medical Media]. (2011, January 14). Liver Biopsy [Video File]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mnHPx5XEvfQ
Photo
- Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2016). Image: Normal and Fatty Liver. Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/home/ovc-20211638


